Periodic Table... A SUMMARY
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic numbers, electron configurations (electron shell model), and recurring chemical properties. Elements are presented in order of increasing atomic number (the number of protons in the nucleus). The standard form of the table consists of a grid of elements laid out in 18 columns and 7 rows, with a double row of elements below that. The table can also be deconstructed into four rectangular blocks: the s-block to the left, the p-block to the right, the d-block in the middle, and the f-block below that.
The rows of the table are called periods; the columns are called groups, with some of these having names such as halogens or noble gases.
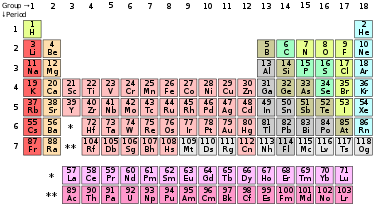 |
| Standard 18-column form of the periodic table |
HERE GOES A TABULAR REPRESENTATION OF THE CLASSIFICATION OF THE ELEMENTS IN THE PERIODIC TABLE:
Group number
|
Type of element
|
Some examples
|
Physical properties
|
Chemical properties
|
|||
1
|
Alkali metals
|
|
malleable, ductile, good
conductors of heat and electricity, softer than most other metals
|
very reactive metals, only
one electron in their outer shell, explode if they are exposed to water.
|
|||
2
|
Alkaline Earth
|
|
have an oxidation
number of +2, making them very reactive.
|
||||
3
|
Transition metals
|
Silver
|
Ununbium
|
both ductile and
malleable, and conduct electricity and heat. Noteworthy elements are iron,
cobalt, nickel- only ones to produce magnetic field
|
Valence
electrons in more than one shell that is why they have several oxidation
states
|
||
13.14.15
|
Other metals
|
|
ductile and malleable,
solid, have a relatively high density, and are opaque.
|
do not exhibit
variable oxidation states
|
|||
Metalloids
|
|
Have properties of both metals and non-metals. Some of the
metalloids, such as silicon and germanium, are semi-conductors. This means
that they can carry an electrical charge under special conditions. This
property makes metalloids useful in computers and calculators.
|
|||||
14-16
|
Non-metals
|
|
not able to conduct
electricity or heat, very brittle,neither ductile nor malleable, exist either
as gases (such as oxygen) or solids (such as carbon)at room temperature, no
metallic luster, and do not reflect light.
|
have oxidation numbers
of ±4, -3, and -2.
|
|||
17
|
Halogens
|
|
The halogens exist, at room temperature, in all three states of
matter:
Solid- Iodine, Astatine
Liquid- Bromine
Gas- Fluorine, Chlorine
|
Compounds containing
halogens are called "salts". All halogens have 7 electrons in their
outer shells, giving them an oxidation number of -1.
|
|||
18
|
Noble gases
|
|
Gaseous
in nature
|
oxidation number of 0
prevents the noble gases from forming compounds readily.
|
|||
3 (6th and 7th period)
|
Rare Earth Metals
|
Lanthanide
series
|
Actinide
series
|
The Rare Earth Elements are made up of two series of elements, the Lanthanide and Actinide Series.
| One element of the lanthanide series and most of the elements in the actinide series are called trans-uranium, which means synthetic or man-made. | ||

Comments
Post a Comment